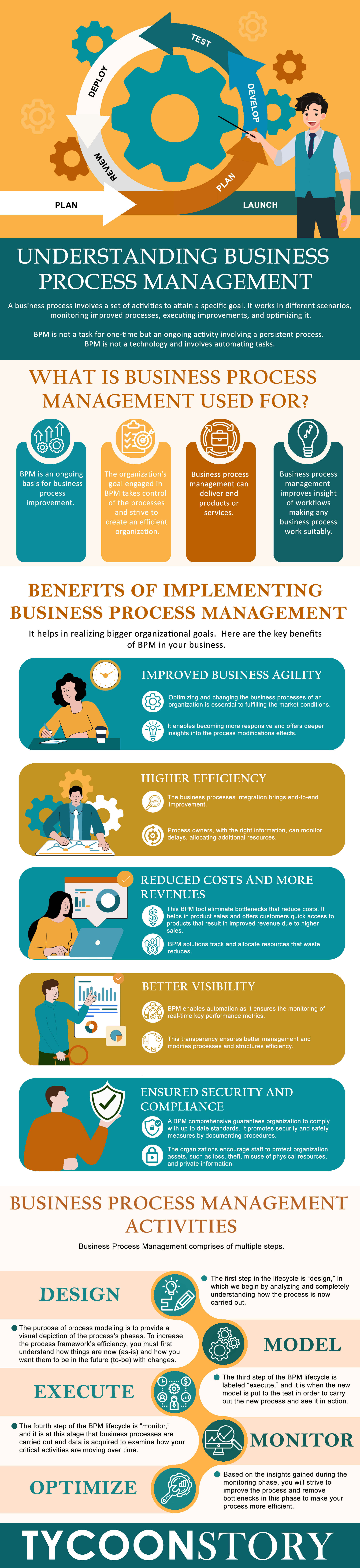
BPM, Business process management, is a way of improving the business process by analyzing it from end to end. A business process involves a set of activities to attain a specific goal. It works in different scenarios, monitoring improved processes, executing improvements, and optimizing it. BPM is not a task for one-time but an ongoing activity involving a persistent process. BPM is not a technology and involves automating tasks.
What is BPM used for?
BPM is an ongoing basis for business process improvement. The organization’s goal engaged in BPM is to take control of the processes and strive to create an efficient organization. They can deliver end products or services. It improves insight of workflows, making any business process work suitably. Thus, BPM supports organizational leaders in achieving operational efficiencies.
Business Process Management Activities
Business Process Management comprises of multiple steps. It includes designing, executing, modeling, optimization, monitoring, analyze, implementing, model, manage, automate, monitor, and so on.
Business Process Management allows organizational leaders to get a grasp of various processes within their organization. It helps them to analyze and improve on an ongoing basis. The end-to-end processes of the business improve individual tasks, giving the ability to enjoy greater outcomes. BPM, well-executed, reduces waste, saves time, cuts down errors, and generates better products and services. It delivers improvements continually.
BPM is not a one-shot task. It goes on as a process, continuously allowing the organizational leaders to manage. They keep optimizing, focusing the end-to-end business processes introducing new opportunities and pressures. With emerging technologies, they work better, and within the overall process, it automates tasks.
What BPM is not?
Not task management. Task management refers to organizing or handling a set of activities. Business process management is a repetitive and ongoing process that follows a predictable process or pattern management.
Not a software product. BPM tools are available to help implement automated and standard business processes. It helps businesses automate complex and repetitive business processes. However, BPM is not a software product.
When do organizations implement business process management?
- Business processes require more legacy applications for completion.
- Dynamic processes requiring regulatory compliance, such as a change in customer information management in privacy or finance laws.
- Business processes offer quick turnarounds as it involves manual handling.
- Complex processes that need coordination and orchestration across various units, functional departments, divisions, or workgroups.
Advantages of Implementing Business Process Management
BPM helps organizations in moving towards digital transformation. It helps in realizing bigger organizational goals. The key benefits of BPM in your business:
- Improved Business Agility: Optimizing and changing the business processes of an organization is essential to fulfilling the market conditions. It allows organizations to implement changes, pause the processes, and re-execute them. It enables becoming more responsive and offers deeper insights into the process modifications effects.
- Higher Efficiency: The business process integration brings end-to-end improvement. Process owners, with the right information, can monitor delays, allocating additional resources. Removal and automation of repetitive tasks add to efficiencies.
- Reduced Costs and More Revenues: This BPM tool eliminate bottlenecks that reduce costs. It helps in product sales and offers customers quick access to products that result in improved revenue due to higher sales. BPM solutions track and allocate resources that waste reduces.
- Better Visibility: BPM enables automation as it ensures the monitoring of real-time key performance metrics. This transparency ensures better management and modifies processes and structures efficiency.
- Safety, Compliance, and Security: A BPM comprehensive guarantees organization to comply with up-to-date standards. It promotes security and safety measures by documenting procedures. The organizations encourage staff to protect organization assets, such as loss, theft, misuse of physical resources, and private information.